Lesson
[Definition]
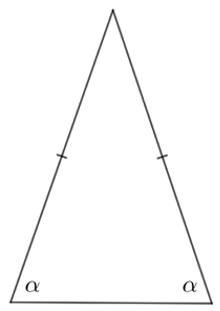
Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides and two equal base angles
Example
Match the numbered statements in Column X with the letters allocated to the diagrams in Column Y by classifying according to sides or angles.
Explain your answers.
Column X
|
Column Y
|
||
1 |
An acute triangle has 3 acute angles |
A |
|
| 2 |
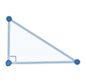
A right triangle has 1 right angle |
B | |
| 3 |
An obtuse triangle has 1 obtuse angle |
C |
|
| 4 |
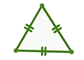
An equilateral triangle has 3 congruent sides |
D | |
| 5 |
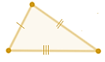
An isosceles triangle has at least 2 congruent sides |
E |
|
| 6 |
A scalene triangle has no sides of equal length |
F | |
Solution
|
1-E All angles are less than 90° |
2-A One angles is equal to 90° |
3-B One angle is greater than 90° |
|
4-C All sides are of equal length |
5-F Two sides are of equal length |
6-D None of the sides are equal length |
Question
A triangle’s largest angle is 2.5 times larger than the smallest angle. If the third angle is 40°, what type of triangle is it?
Explanation
Given the information, we can create an equation and solve.
2.5x + x +40 = 180
3.5x = 140
x = 40
Therefore, the angles are 100°, 40°, 40° and the triangle is isosceles.
Want a FREE question and answer worksheet?
Download Your Free Types of Triangles Maths Worksheet With Answers PDF Here >>